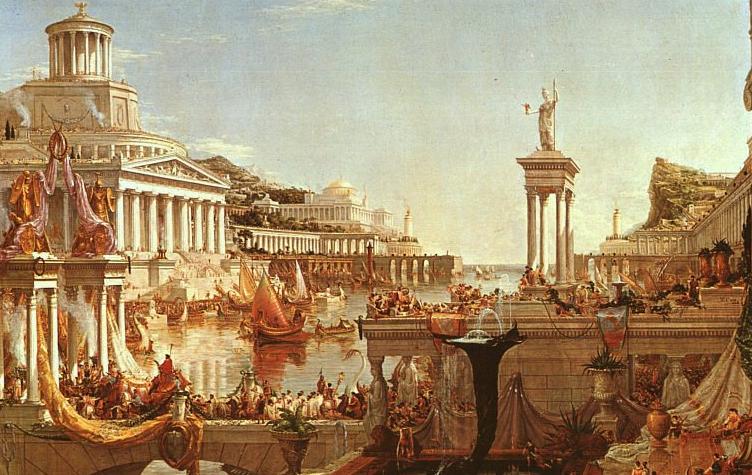
Life in the Roman Empire was a complex tapestry of societal norms, cultural practices, and political structures that evolved over centuries. From its humble beginnings as a small city-state on the Italian peninsula to its zenith as one of the greatest empires in history, Rome’s influence spread far and wide, shaping the world we know today.
At the heart of Roman society was the concept of citizenship. Citizens enjoyed certain rights and privileges that non-citizens did not have, such as voting in elections and holding public office. However, citizenship was not easily obtained; only free-born males who met certain criteria could become citizens. Women, slaves, and foreigners were excluded from this privileged status.
Social class also played a significant role in Roman society. The elite patrician class held most of the power and wealth, while the plebeians made up the majority of the population but had limited rights and opportunities for advancement. Slaves were at the bottom rung of society, considered property rather than people.
Despite these divisions, Romans prided themselves on their sense of community and shared identity. Public spaces like forums, baths, and theaters served as gathering places where citizens could socialize, conduct business, or attend performances. Festivals and religious ceremonies provided opportunities for people to come together to celebrate their shared heritage.
Roman culture was a rich tapestry woven from diverse influences. The Romans borrowed heavily from Greek art, literature, philosophy, and architecture but added their own unique twist to create something distinctly Roman. They excelled in engineering feats such as aqueducts, roads, bridges, and amphitheaters that showcased their ingenuity and ambition.
Religion played a central role in Roman life. The Romans worshipped a pantheon of gods and goddesses who controlled various aspects of nature and human affairs. Temples dedicated to these deities dotted the landscape throughout the empire where rituals were performed to ensure divine favor.
The Roman legal system was another cornerstone of society that helped maintain order and justice within the empire. Laws were codified into written statutes that applied equally to all citizens regardless of social status or wealth. Judges presided over trials where evidence was presented before rendering verdicts based on established legal principles.
As Rome expanded its borders through conquests across Europe,Mediterranean Africa,and Asia,the empire became increasingly diverse with different cultures blending together under Roman rule.This multiculturalism enriched Roman society with new ideas,languages,and customs that influenced art,literature,Themes in Roman Society and Culture: An Introduction to Ancient Rome 2nd Edition was a dynamic mosaic shaped by centuriesof tradition,cultural exchange,and political upheaval.Lifeintheempirewas marked by social hierarchies,political intrigue,and artistic achievementsthat continue to inspire us today.